Genes Contain Instructions For Assembling
16 How do genes direct the product of proteins?
The information to make proteins is stored in an organism's DNA. Each protein is coded for by a specific section of DNA called a gene. A gene is the section of DNA required to produce 1 protein. Genes are typically hundreds or thousands of base of operations pairs in length because they code for proteins made of hundreds or thousands of amino acids.
Most genes contain the data needed to make functional molecules called proteins. A few genes produce other molecules that assist the jail cell gather proteins. The journey from gene to protein is complex and tightly controlled within each jail cell. It consists of ii major steps: transcription and translation. Together, transcription and translation are known as cistron expression.
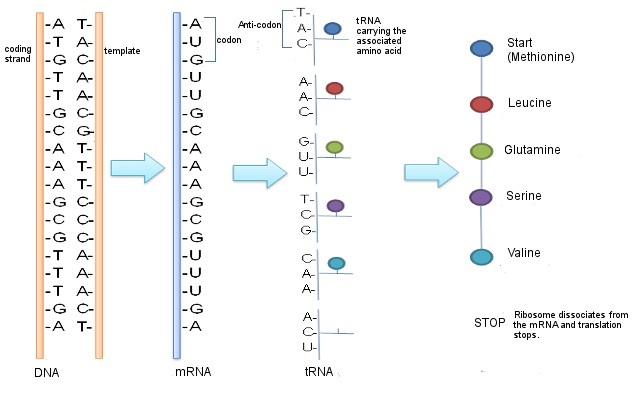
During the process of transcription, the data stored in a gene's Deoxyribonucleic acid is transferred to a similar molecule called RNA (ribonucleic acid) in the cell nucleus. Both RNA and Dna are made up of a chain of nucleotide bases, but they have slightly different chemical properties. The type of RNA that contains the information for making a protein is called messenger RNA (mRNA) because information technology carries the information, or message, from the DNA out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm.
Translation, the second stride in getting from a cistron to a protein, takes place in the cytoplasm. The mRNA interacts with a specialized complex called a ribosome, which "reads" the sequence of mRNA bases. Each sequence of three bases, called a codon, usually codes for one particular amino acid. Recollect that amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. A blazon of RNA called transfer RNA (tRNA) assembles the protein, one amino acrid at a time. Protein assembly continues until the ribosome encounters a "stop" codon (a sequence of three bases that does non code for an amino acrid).
The flow of information from DNA to RNA to proteins is one of the fundamental principles of molecular biology. It is so important that information technology is sometimes chosen the "central dogma."
References
Unless otherwise noted, images on this folio are licensed under CC-By 4.0 by OpenStax.
"What are proteins and what do they exercise?" by U.S. National Library of Medicine is in the Public Domain
Genes Contain Instructions For Assembling,
Source: https://openoregon.pressbooks.pub/mhccbiology102/chapter/how-do-genes-direct-the-production-of-proteins/
Posted by: mcguiganselse2000.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Genes Contain Instructions For Assembling"
Post a Comment